







Welcome Back
Sign in to be closer to your community!
Follow other divas, like and comment
on their posts, message them, and see
who loved your posts!
Invalid username or password
You have not verified your account by clicking on the link we sent you via email. Please check your email folders (including your Spam folder) and click on the verify link sent.
Email is required
Password is required








Join FashionPotluck.com
Create your own profile in order to create content, follow other divas and like their posts, use our own messenger, and be a part of a growing international women community!
WELCOME TO OUR COMMUNITY
Fashion Potluck -
the first social media
platform for women.
You are free to read/watch & create content,
express your true self, and interact with others.
Join for free
Already a member? Log in here.
Purchase Alert
Dear Queen, you can only buy from one seller at the time. Please finish this purchase first in order to buy from another FP member
Comments
Please select one platform to continue
Please select one platform to continue
Please select one platform to continue
Please select one platform to continue
Please select one platform to continue
Please select one platform to continue
Please select one platform to continue
Please select one platform to continue
EDITOR APPROVED
You are wondering what is this 'Editor Approved'?
Well, this is pretty awesome! In order for the post to qualify and receive this accolade, it has to have a minimum of 700 words and two images (at least one original).
Receiving this accolade means two things: 1) Your content is amazing! Good job! 2) Your content qualifies for our monetization program. Every week two of the most read posts receive monetary rewards.
Have the badge & want to monetize your content?
LIFESTYLE
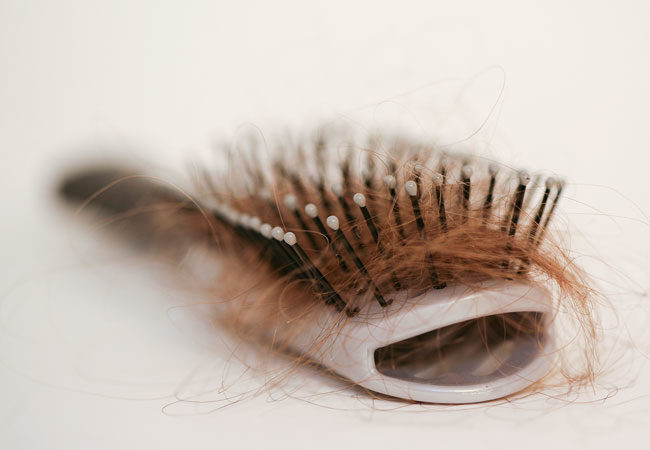

Every day you lose a certain amount of hair. It's normal to shed between 50 and 100 hairs a day, but when you lose more than that it can indicate certain health problems. Pattern baldness is the most common cause of both male and female hair loss. But there is a wide range of other reasons why you are losing your hair.
Below are 7 medical problems that can lead to hair loss.
1. Alopecia
Alopecia is a common cause of hair loss. There are two main types of alopecia called alopecia areata and androgenic alopecia. Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition in which your immune system attacks healthy hair follicles and causes severe hair loss. Androgenic alopecia is a genetic condition that often runs in families.
Because of his condition, you can start losing hair in your 20s or even earlier. Both these conditions cause hair thinning, balding, or patches of hair loss on the head and within the body. Both these conditions require medical treatment, otherwise, you risk losing all your hair.
2. Thyroid problems
Thyroid problems are often associated with hair loss. Both hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can result in severe hair shedding. This happens because thyroid problems contribute to major hormonal imbalances, disrupting nearly every function in your body.
To stop hair loss associated with thyroid problems, it is important to get qualified medical help and manage the condition. Treatment helps balance the hormones and preserve the health of your hair.
3. Nutrient deficiency
Your body needs a variety of nutrients and minerals to function properly. The deficiency of one of them can worsen your overall well-being and cause hair loss. To preserve the health of your hair you need to consume enough healthy foods like fresh fruits and vegetables, cereals, healthy fats, and proteins. A nutrient-rich diet is the best way to ensure the health of all body organs and systems.
You may also ask your doctor about nutrient-deficiency testing. This can help you understand which exact nutrient your body lacks and replenish its levels.
4. Severe stress
Severe stress can cause a variety of health problems, including hair loss. Both physical and emotional stress can contribute to hair shedding. You may start losing your hair after a serious surgery or injury. A traumatic and stressful event like bankruptcy, divorce, or the death of a loved one can disrupt the normal cycle of hair loss. This results in the significant thinning of the hair and hair loss. The effect of stress can be temporary and permanent.
If you start losing your hair because of severe stress, consult your healthcare provider. The specialist can recommend stress management strategies and hair restoration procedures to improve the appearance of your hair.
5. Skin infections
There are several skin infections that can lead to major hair loss. The most common include ringworm, folliculitis, and seborrheic dermatitis. Ringworm is a fungal infection that causes patches of hair loss on the scalp. Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicle that looks like acne. Without treatment, the inflammation can aggravate and damage the follicle permanently. Seborrheic dermatitis is an infection that causes scaly inflamed patches of the skin and hair loss.
Any of these conditions need to be checked by your doctor. Only a specialist can make a diagnosis and prescribe an appropriate treatment.
6. Medications
All medications have a wide variety of side effects. They can cause dizziness, headaches, muscle spasm, and vomiting. But some medications can contribute to hair loss. Some of the widespread medications that cause hair loss include oral contraceptives, antidepressants, blood-thinning medications, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Consuming too much vitamin-A (retinoids) can also contribute to excessive hair shedding.
7. Autoimmune diseases
Diabetes and lupus are autoimmune conditions that can cause hair loss. Diabetes can alter the cycle of hair growth and stop new hair from forming. This results in the loss and poor growth of your hair. Lupus causes a widespread inflammation that can affect your scalp and hair follicles. Over time, lupus leads to thinning of the hair on your scalp and can contribute to baldness. Loss of eyebrows, eyelashes, beard, and body hair also is possible.
-
 Rosalia T :
Rosalia T :
Super interesting read! I actually experience a lot of hair loss after having COVID. Many people told me it was one of the side effects after
Comments
Related Posts
- AI Agents in Customer Support: Moving Beyond Chatbots by Ella Taylor 0
- What to Expect From a Consultation With an Immigrant Attorney? by Monica Quinn 0
- 6 Habits That Can Worsen Migraines by Monica Quinn 0
More Posts
Vote content out
Reason for voting this content out?
Reason for voting this content out?

 Login with Google
Login with Google Login with Twitter
Login with Twitter






 by
by
Add Comments